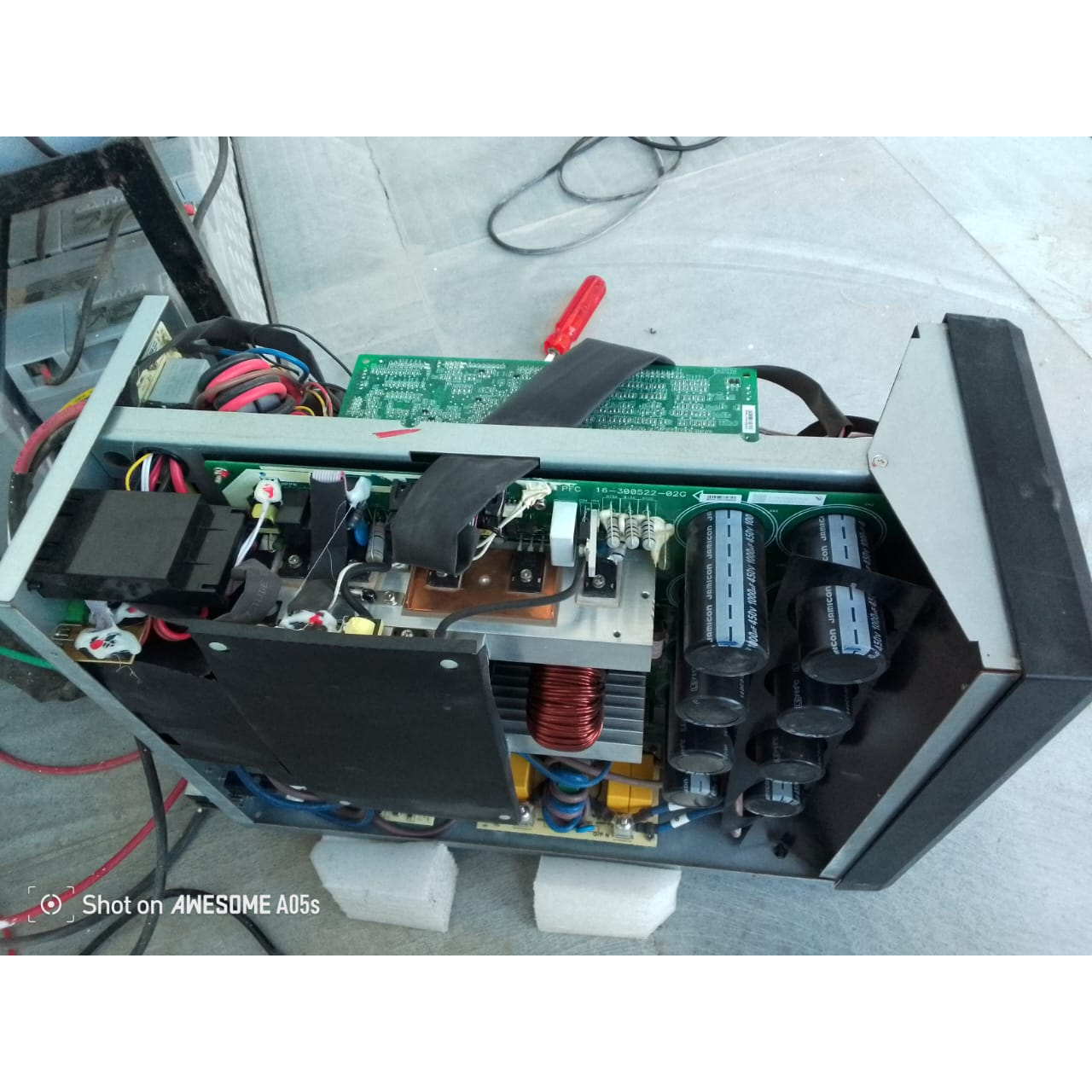
UPS REPAIR Repairing a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply), especially a high-capacity unit like the 30 kVA model from Vertiv, requires a good understanding of both electrical systems and the specific components of the UPS. Here’s an overview of the general repair process for a UPS and common issues you might face: Common UPS Problems Battery Issues: Symptoms: UPS not providing backup power, shorter backup times. Possible Causes: Dead or degraded batteries, loose battery connections. Repair: Replacing the battery pack or recharging the batteries if they are not completely worn out. Overheating: Symptoms: UPS shuts down due to excessive heat, fans running continuously. Possible Causes: Blocked ventilation, faulty fan, poor airflow. Repair: Cleaning vents and fans, replacing defective fans, or ensuring proper placement for airflow. Power Surge or Overload: Symptoms: Frequent tripping, UPS not holding a charge. Possible Causes: Too many devices connected, faulty internal circuitry. Repair: Reducing load or identifying faulty components and replacing them. Inverter or Rectifier Failure: Symptoms: UPS fails to convert DC to AC power, no output power during battery operation. Possible Causes: Failed inverter/rectifier board. Repair: Replacing or repairing the inverter/rectifier board. Control Circuit Problems: Symptoms: UPS not starting, abnormal display readings, failure to operate normally. Possible Causes: Faulty microprocessor or control board. Repair: Replacing or reprogramming the control board. Electrical Failures: Symptoms: No power output, UPS won’t turn on, circuit board failure. Possible Causes: Faulty capacitors, transformers, or circuit breakers. Repair: Diagnosing the faulty components and replacing them. Steps for UPS Repair: Diagnosis: Initial Inspection: Check for obvious signs of damage (e.g., burnt components, loose connections). Error Codes/Alarms: Look at any display indicators or error codes on the UPS. Check Battery Health: If the issue is power-related, test the batteries and make sure they are holding a charge. Load Testing: Check the UPS under load to confirm whether it can support connected equipment. Power Down and Safety: Always ensure the UPS is powered down and disconnected from the grid before opening it up for repairs. Use safety gear like gloves and safety glasses, as UPS systems contain high-voltage components. Component Inspection and Replacement: Batteries: Test individual batteries and replace any that show signs of failure. Fans and Vents: Clean fans and air filters; replace any faulty fans. Inverter/Rectifier Circuit: Test for correct DC-AC conversion. Replace the board or components if necessary. Control Boards: Inspect for visible damage, burned areas, or faulty connections. Reassembly and Testing: After replacing faulty parts, reassemble the UPS. Perform a full function test under load to ensure that the UPS is working properly. Regular Maintenance: Even after repair, ensure regular maintenance to extend the lifespan of the UPS. Clean dust, check battery voltage periodically, and run load tests regularly.
Chat with us on WhatsApp
×
This is your website preview.
Currently it only shows your basic business info. Start adding relevant business details such as description, images and products or services to gain your customers attention by using Boost 360 android app / iOS App / web portal.
https://locations.universalpower.co.in/bhiwadi/latest-update/ups-repair-repairing-a-ups-uninterruptible-power/1322
UPS REPAIR Repairing a UPS (Uninterruptible Power...

2025-03-27T06:02:38
UPS REPAIR Repairing a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply), especially a high-capacity unit like the 30 kVA model from Vertiv, requires a good understanding of both electrical systems and the specific components of the UPS. Here’s an overview of the general repair process for a UPS and common issues you might face: Common UPS Problems Battery Issues: Symptoms: UPS not providing backup power, shorter backup times. Possible Causes: Dead or degraded batteries, loose battery connections. Repair: Replacing the battery pack or recharging the batteries if they are not completely worn out. Overheating: Symptoms: UPS shuts down due to excessive heat, fans running continuously. Possible Causes: Blocked ventilation, faulty fan, poor airflow. Repair: Cleaning vents and fans, replacing defective fans, or ensuring proper placement for airflow. Power Surge or Overload: Symptoms: Frequent tripping, UPS not holding a charge. Possible Causes: Too many devices connected, faulty internal circuitry. Repair: Reducing load or identifying faulty components and replacing them. Inverter or Rectifier Failure: Symptoms: UPS fails to convert DC to AC power, no output power during battery operation. Possible Causes: Failed inverter/rectifier board. Repair: Replacing or repairing the inverter/rectifier board. Control Circuit Problems: Symptoms: UPS not starting, abnormal display readings, failure to operate normally. Possible Causes: Faulty microprocessor or control board. Repair: Replacing or reprogramming the control board. Electrical Failures: Symptoms: No power output, UPS won’t turn on, circuit board failure. Possible Causes: Faulty capacitors, transformers, or circuit breakers. Repair: Diagnosing the faulty components and replacing them. Steps for UPS Repair: Diagnosis: Initial Inspection: Check for obvious signs of damage (e.g., burnt components, loose connections). Error Codes/Alarms: Look at any display indicators or error codes on the UPS. Check Battery Health: If the issue is power-related, test the batteries and make sure they are holding a charge. Load Testing: Check the UPS under load to confirm whether it can support connected equipment. Power Down and Safety: Always ensure the UPS is powered down and disconnected from the grid before opening it up for repairs. Use safety gear like gloves and safety glasses, as UPS systems contain high-voltage components. Component Inspection and Replacement: Batteries: Test individual batteries and replace any that show signs of failure. Fans and Vents: Clean fans and air filters; replace any faulty fans. Inverter/Rectifier Circuit: Test for correct DC-AC conversion. Replace the board or components if necessary. Control Boards: Inspect for visible damage, burned areas, or faulty connections. Reassembly and Testing: After replacing faulty parts, reassemble the UPS. Perform a full function test under load to ensure that the UPS is working properly. Regular Maintenance: Even after repair, ensure regular maintenance to extend the lifespan of the UPS. Clean dust, check battery voltage periodically, and run load tests regularly.
2025-03-27T06:02:38
Keywords
- ups perform
- ups systems
- ups heres
- safety glasses
- safety gear
- show signs
- error codes
- display indicators
- obvious signs
- battery operation
- convert dc
- completely worn
- battery pack
- common issues
- specific components
- electrical systems
- good understanding
- vertiv requires
- 30 kva model
- highcapacity unit
- output power
- ac power
- powerrelated test
- faulty components
- faulty microprocessor
- failure fans
- ups repair repairing
- circuit board failure
- identifying faulty components
- air filters replace
- airflow power surge
- full function test
- vents clean fans
- faulty connections reassembly
- faulty capacitors transformers
- control boards inspect
- ensuring proper placement
- general repair process

Submit Your Enquiry